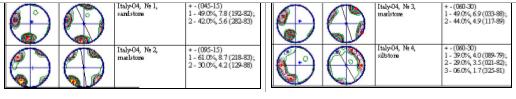
Table 1. Points of supervision of the
maximal compression axis of the palaeostress field at the end of Mesozoic -
beginning of Cenozoic.
ALPINE PALAEOSTRESS OF THE
BELOUSOV T.P.
During 2004, we accomplished several tectonophysical
routes on the left side of the
The area of
In carbonate to thickness of the Tuscan cover in
adjournment of Sillano formation (Late Cretaceous - Early Eocene) were
incorporated four points of supervision, in each of them it is made 100 gauging
elements of attitude planes joints superficial adjournment. Basing on
experience of studying in various regions of the Earth of systems of easing in
young sedimentary adjournment, we accept, that directions of the future initial
fracturing are pawned at initial stages of lithogenesis horizontally deposited
sediments owing to their internal instability. The instability connected to influence
of an existing field of palaeostress, results to localization shift plastic
deformations in the narrow regularly located connected microzones, normal in a
plane of a sedimentary layer. Microzones of localization shift deformations
with increase of a degree of lithification deposits pass a skeleton of the
future in initial joints.
On the basis of the analysis of pattern initial
interstratum fracturing sedimentary breeds of Sillano formation the direction
of compression was reconstructed within the limits of researched area of
Table 1. Points of supervision of the
maximal compression axis of the palaeostress field at the end of Mesozoic -
beginning of Cenozoic.

Other area of Italy within the limits of which
supervision in two points it was investigated fracturing sedimentary breeds
Quarternary of age the island Ischia which is settled down approximately in 30
km west from Naples. The island is combined with volcanic lavas and
Pleistocene-Holocene layered pyroclastic rocks. Reconstruction of the intense
condition has shown, that in the northwest part of island on the Quarternary
stage of his formation compression had latitudinal direction. Thus, in area of
Results of field tectonophysical researches in area
of