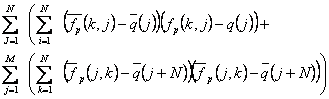THE STATISTICAL MATHEMATICAL
METHODS OF PROCESSING THE GRAVITY AND AIRBORNE GAMMA RAY SPECTRUM DATA FOR
EVALUATING AND PROSPECTING MINERAL RESOURCES
1NGUYỄN TÀI THINH, 2NGUYỄN
THẾ HÙNG
1Việt Nam Association of
Geophysicists, 18 Hoàng Quốc Việt, Hà Nội;
2Division of Geophysics,
Km.9, Nguyễn Trãi Road, Thanh Xuân, Hà Nội.
Abstract: This paper
presents a complex of methods of processing and analyzing the gravity and
airborne magnetic-gamma ray spectrometer data, which are based on the methods
of mathematical statistics for evaluation and prospecting of mineral resources.
These methods are formed on the basis of results of researches and applications
that were carried out by the authors in the Division of Geophysics during
recent years.
The
statistical methods of processing and analyzing the gravity and airborne gamma
ray spectrometer data consists mainly of defining the statistical
characteristics and the correlation functions of geophysical fields; applying
the filtration for analyzing the geophysical field components; determining the
multisignal anomalies by geophysical data; pattern recognizing by using sample
mines and etc.. The used algorithms are mainly in softwares Coscad 8.0, Coscad
3D (Russian Federation,
2002), Potential Field (USA,
1995), ER Mapper (Australia,
1995), etc. in combination with some specific support softwares written by the
authors.
In this paper
the authors outline also some results, as an illustrating example of using the
above mentioned complex of methods for processing and analyzing the gravity and
airborne magnetic - gamma ray spectrometer data on scale of 1/50,000 applied in
the Tiên Phước area, Quảng
Nam Province
to evaluate the perspective of mineral resources in this area. The results of
processing allow to contour 4 primary gold perspective regions: Núi Nưa of Tiên
Hiệp commune, Thôn Ba, Thôn Bốn of Trà Đốc commune, Vĩnh Ninh and the region of
potassium feldspar perspective about east of Hưng Nhượng. The ground detailed
assessment has showed some gold sulphide-quartz zones of large size and high
gold concentration (about of 1.0 - 102 g/t Au).
The obtained
in the Tiên Phước area results prove the reasonableness and the effectiveness
of the complex of applicated methods.
I. INTRODUCTION
In Việt Nam, the gamma-ray spectrometer and gravimeter
studies at the scale of 1/50,000 up to 1/25,000 have been carried out about
over 100,000 km2, covering almost the region of from Thanh Hóa to
Bình Thuận, Tây Nguyên area and some the mountainous area of North Việt Nam.
The obtained data were analysed for different purposes in the time of report
for the projects. Therefore, the exploitation and synthesis of information is
still in the limited level.
The study for finding the methods of processing,
analyzing airborne gamma-ray spectrometer and gravimeter data were started
since 1995 by Nguyễn Tài Thinh, Nguyễn Thế Hùng, Đỗ Tử Chung, Võ Thanh Quỳnh,
Nguyễn Tuấn Phong, Doãn Ngọc San,... The results of these studies were applied
in different levels. Among them, the complex of methods of processing, analyzing
the airborne gamma-ray spectrometer and gravity data for geological and mineral
resource investigation on the basis of statistical mathematics, carried out by
Nguyễn Tài Thinh, Nguyễn Thế Hùng and etc., has been widely used and get the
active results in the geological interpretation and mineral exploration.
The results of analyzing the geophysical data by
statistical maths during recent years play important role in the geological and
mineral investigation, especially in the finding new deposits, such as uranium
in Quảng Nam, fluorite in Bình Định,
magnesite in Gia Lai, gold and tin mines in Nghệ An, Quảng Bình, Huế, Lâm Đồng,
etc. and many prospecting regions.
II. ESSENTIAL STATISTICAL PROCESSING METHODS
1. Main parameters of gamma ray spectrometer
anomaly
The statistical parameters used in the geological
and mineral resource investigation are as follows:
- Relative radiation
parameters (JK, JTh, JU): Radiation parts of the
radioactive elements in total radiation field. This parameters represent the
nature of radiation field.
- Ratio of contents of
the radioactive elements: In the primary rocks the correlation between radioactive elements is
nomal, so as the content ratios between them vary in a small range. But in the
altered rocks these ratios change visibly. The ratios used in the processing
are: qTh/qU; qK/qTh; qU/qK
- Multi-component
parameter (F): Multi-component parameter is calculated by the formula: F = qU.qK/
qTh
Zones of high multi-component parameters often
present altering rocks. For this reason the multi-component parameter is
considered as prospective index.
- Dominal parameters: Di = qi.qi
/ qj.qK. The altered processes of the rocks will change
the content of their radioactive elements. The content of some elements will
increase while the content of some other decreases. Dominal parameters (DU,
DTh, DK) allow to define these changes and calculated by
formulae:
Above-based content Δqij is calculated by:
Δqij = qi2 - kij . qi
Where: Δqij
- above-base content of the radioactive element - i; qi - content of the radioactive element - i; kij
- base value of the ratio of the element couple - i and - j.
2. Main statistical processing methods
Basic statistical performances: The calculation of statistical feature of the
gamma ray spectrometer and gravimeter data is a necessary step for defining the
used methods and sequence of processing. The basic statistical performances
include mathematical expectation, variances, standard deviation, asymmetries,
variant range, gradient, radius of correlation … and other features, such as:
autocorrelation function D(K, M); autocorrelation function between two fields
B(m); autocorrelation and structure-correlation function RR(L); spectrum analysis of the geophysical fields….
Separation of the field
into the different components: Optimal filter: energy filter, Vine - Conmogorop
filter; component analysis method.
Detection of multisignal
anomaly: The
use of autocorrelation and structural correlation functions (ACF và SCF) as
above mentioned allows to detect the multisignal anomalies. In prospecting
(exploratory) geophysics under weak anomaly it is accepted to count a signal
which is commensurable on amplitude with a level of disturbance or is lower
than this level and its authentic visual discovery is practically impossible.
Classification methods: K-mean classification
method; Multi-dimensional Classifi-cation Method.
Method
of pattern recognization: The problem is presented
such as there should be recognized by pattern of the multi-signal anomalies
based on the data set F(i,j), i =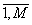 , j =
, j = 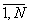 , with size of M*N points, where M: number of points on
profile, N: number of profiles.
, with size of M*N points, where M: number of points on
profile, N: number of profiles.
We suppose that, the window size is of M*N points
and inclination of zero, the mathematic model of field consists of signal
(anomaly) A(i,j) and disturbance n(i,j). The disturbance conforms to
p-dimensional standard distribution with p: dimensional average vector equal 0
and correlation matrix S.
Therefore it should be used statistic T2
and distribution of Fisher:
F = 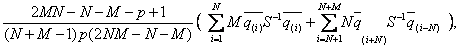
Where :
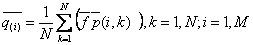 : valuation of different vectors of averages along the
columns in the window;
: valuation of different vectors of averages along the
columns in the window;
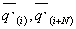 row vectors;
row vectors;
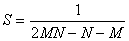
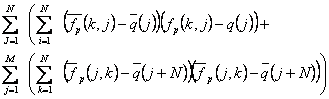
is valuation of total correlation matrix by columns
and rows.
The hypothesis is considered as truth when F < Flim, where Flim:
critical value of Fisher distribution with freedom orders g1, g2:
g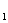 =
=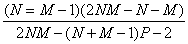 ; g
; g = 2NM – N +M – P +1
= 2NM – N +M – P +1
The truth of H0 - hypothesis confirms
that, the centre of window is the same anomaly. By moving the window along all
the profiles we should contour the anomalies in the investigation area.
III. SOME RESULTS APPLIED FOR EVALUATION OF
PRIMARY GOLD PERSPECTIVE IN TIÊN PHƯỚC AREA, QUẢNG NAM PROVINCE
The Tiên Phước area is about of 1000 km2
in area, located in the Tiên Phước District, Quảng Nam Province. There are many geological
investiagation and mineral resource evaluation projects in the scale of from
1:1,000,000 to 1:50,000 - whole area, up to 1:10,000 to 1:5,000 - in some localities.
In this area some mines of industrial value were
discovered, such as the Bồng Miêu gold mines, that many years has been
exploited, the Trà Dương gold mine and other primary gold occurrences, the Tiên
An graphite mine, the Tiên Hiệp postassium feldspar mine, etc.. Almost
geologists have been considering the Tiên Phước area as primary gold
perspective place, but it still is not sufficiently evaluated because of the
complicated topographical conditions, geological features, etc..
To evaluate the primary gold perspective of this
area, the authors of this paper carried out the processing of the airborne
gamma-ray spectrometer data obtained by the Division of Geophysics at 1/25,000
scale, basing on the complex of above mentioned methods.
1. Geological, geophysical, mineral features
of Tiên Phước area
Geological
and geophysical features: Geological formations in
Tiên Phước area differ by their physical charateristics [8]. There are mainly
metamorphic rocks of the Khâm Đức Formation (MP kđ), including biotite schist, graphite schist, feldspar quartz
schist of the Lower Subformation, distributed in continuous bands, extending
from the east to the west of the central part of the area. These rocks are
characterized by the positive magnetic anomalies, low intensity ∆T = -30 ¸ 20 nT, rather high gamma
spectrometer fields, of complex structure: Iγ = 3.5 ¸ 10 µR/h, qth =
10 ¸ 35
ppm, qu = 4 ¸ 13.5 ppm, qk = 0.5 ¸ 2.7 %, in special, rather
high qth/qu and qu/qk ratios,
while qk/qth is lower: qth/qu
= 3.0 ¸ 30;
qu/qk = 5 ¸ 8; qk/qth < 0.2.
The amphibole schist, amphibole gneiss schist,
biotite gneiss schist, biotite plagiogneiss of the Middle Subformation are
located in the north and south area, differing from rocks of the Lower
Subformation by complex variable magnetic fields ∆T = -140 ¸ 100 nT, rather low gamma
spectrometer fields: Iγ = 1 ¸ 3 µR/h, qth= 3 ¸ 9 ppm, qu= 2 ¸ 4 ppm, qk =
0.25 ¸
0.75 %.
Magmatism appears in the form of small-sized
massifs, including: biotite-hornblende granodiorite of the Quế Sơn Complex
(GDi/P2-T1 qs),
located at the north and west peripheries in the form of small massifs, with
magnetic field intensity ∆T = -40 ¸ 30 nT, rather high gamma spectrometer field:
Iγ = 3 ¸ 7
µR/h, qth= 4 ¸ 20 ppm, qu = 4 ¸ 12.5 ppm, qk=
1.0 ¸ 2.5
%.
The dark-coloured porphyritic biotite granite of
the Hải Vân Complex (G/aT3n hv)
appears mainly in the south and northwest, characterized by the magnetic field
∆T = -160 ¸ 130
nT, low gamma spectrometer field: Iγ = 1 ¸ 1.5 µR/h, qth = 3 ¸ 5 ppm, qu =
2.5 ¸ 4.5
ppm, qk = 0.5 ¸ 1.5 %.
The porphyritic granosyenite, syenite rocks of the
Măng Xim Complex are located in the northern periphery, having stable magnetic
field ∆T = -10 ¸ 50 nT, rather high gamma spectrometer field, mainly
of thorium, potassium component: Iγ = 3.5 ¸ 5 µR/h, qth = 5 ¸ 15 ppm, qu =
4 ¸ 6
ppm, qk = 1.0 ¸ 2.5 %.
The faults are clearly represented in the
geophysical fields and of NW-SE, NE-SW, submeridional, subparallel trends. The
special interest is in the II-order fault Long Bình - Núi Chè, of subparallel
trend. It is expressed clearly in the magnetic field in the form of series of
small-sized anomalies, which is the boundary between the northern positive and
southern negative magnetic fields, as well as on the gamma spectrometer field.
This is a thrust fault with the rising northern wing.
Primary
gold mineralization:
- Bồng Miêu gold mine: This mine was discovered
before 1954. At present, the Bồng Miêu Gold Company is exploring and exploiting
it.
According to the data of scale 1/10,000 of the №
501 Enterprise of the Central Việt Nam
Geological Division, the Bồng Miêu gold mine comprises metamorphic rocks of the
Lower Khâm Đức Subformation (MP kđ1) with biotite-garnet
gneiss, amphibole gneiss schist, feldspar-sillimanite-quartz schist. These
rocks form the Bồng Miêu anticlinal. The tectonic faults usually include the rising
and subsiding processes, forming the anticlines, synclines and zones of
breaking bearing quartz veins containing mineralization.
Along the faults are located mineral bodies
consisting of gold-quartz veins of bed, lens and nest forms. The thickness of veins
is about 10 cm to 4 m, extending about 3 km in the parallel direction. The
mineralization control is the Bồng Miêu anticline, having 2 types of ore
bodies: 1. Type of concordance between ore bodies and ore-bearing rocks; 2.
Type of discordance between ore bodies and ore-bearing rocks.
The ore mineral composition is mainly of pyrite,
galenite, hematite, chalcopyrite and pyrrhotine. The gold reserves of this mine
is about 12,233 kg with average content of 14 g/t.
- Trà Dương gold mine: located in the southern
part of the study area, discovered in 1990 year during the geological mapping
of the Tam Kỳ - Hiệp Đức sheet-group at 1/50,000 scale. In the 1991, Mai Thất
[4] carried out the study and detailed evaluation of this mine. The gold mine
is situated in ancient metamorphic rocks of the Khâm Đức Formation. Analytical
results show that the gold content is high, about of 0.8 up to 3.4 g/t. This
mine is considered as of good prospect.
- Trà Giang gold mine: located in Trà My
District, Quảng Nam Province,
situated close to the southern part of area [7] (in the rural zone of the
area).
The structure of the gold mine comprises biotite
gneiss, biotite plagiogneiss, biotite-quartz schist of the Middle Khâm Đức
Subformation (MP kđ2). The
rocks are mainly altered by the chloritization process, penetrated by the
diorite, quartz diorite, horblende granodiorite of the Trà Bồng Complex (Di-GD1/O-S
tb). In the central part occur small
massifs of biotite granite, two-mica
granite of the Bà Nà Complex (G/K bn).
The fault system is mainly in subparallel
direction. The dip angle of the faults are of from 80 to 850. The
width of cataclastic zones is about 70 to 100 m containing gold-sulphide quartz
veins. These faults are the factor controlling and locating the gold ores,
while the faults of NW-SE direction move the system of subparallel faults.
In the mine were detected 6 gold ore bodies,
located in gold quartz dykes. The ore bodies are mainly of band and lens form,
extending discontinuously in the range of from 50 to 300 m, the thickness
varies from 0.2 to 1.2 m and located in the zone of chloritization,
pyritization or along the strike of the schists. The ore mineral component
includes pyrite, magnetite, chalcopyrite, galenite and sphalerite.
The gold content is about 2.4 to 75.5 g/t; silver
content - 2.4 to 31.7 g/t. The supposed reserves for the gold: 3265 kg; for
silver: 3265 kg.
Besides, during the investigation
at the scale of 1/200,000 and 1/50,000 were discovered 4 primary gold
occurrences in the Tiên Lập Commune, and 2 occurences in the Tiên Lanh Commune,
near the left side of the Tranh
River.
2. Some results of analysing the geophysical
data for primary gold evaluation
For the primary gold evaluation of the Tiên Phước
area, the authors have been carrying out the processing and analysis of the
airborne gamma-ray spectrometer data by the above mentioned method system. To
apply the method of pattern recognization 2 well-known primary gold mines were
selected, namely Bồng Miêu and Trà Giang ones.
The signs used for pattern recognization are of 18
parameters: Iγ, qTh, qU, qK, JK,
JU, JTh, F, ΔT, DK, DU, DTh,
qTh/qU, qU/qK, qK/qTh,
Δqkth, Δquk, Δquth.
In the results, 3 types of geophysical anomalies
are contoured, representing different altered processes:
- 1st type
of anomaly: including the anomalies of potassium nature, with low content of
thorium, uranium: qk = 1.4 ÷ 2.2 %, Jk = 0.2 ÷ 0.4, qk/qth
= 0.2 ÷ 0.4, qu = 3 ÷ 4.5 ppm, Ju = 0.3 ÷ 0. 45, qth
= 2 ÷ 5 ppm, F = 1.0 ÷ 1.8. The anomalies of this type may be concerned
with the sulphidization process (type 1a).
In some places, there are anomalies of high
potassium and thorium contents: qk = 2 ÷ 4 %, qth = 15 ÷
25 ppm, F = 0.6 ÷ 0.9. The anomalies of
this type may be concerned with the pegmatite bodies of high potassium (type
1b).
- 2nd type
of anomaly: The nature of this anomaly is mainly of potassium-uranium, Ju –rather high, while thorium
content and other parameters – lower. J = 2 ÷ 4 mr/h, qu = 2 ÷ 4 ppm, sometimes 4 ÷ 6 ppm, qth
= 2 ÷ 6 ppm, qk = 1.0 ÷ 1.6 %, Ju = 0.5 ÷ 0.76, Jth
= 0.2 ÷ 0.45, jk = 0.2 ÷ 0.45, F = 0.6 ÷ 1.8, qk/qth
= 0.2 ÷ 0.4, qu/qk = 6 ÷ 25, qth/qu
= 2 ÷ 5. This type of anomaly may be concerned with the sulphide-quartz
alteration.
- 3rd type
of anomaly: The nature of this anomaly is mainly of thorium-uranium, while
potassium parameter is lower. J = 3.5 ÷ 6.5 mr/h, qu = 5 ÷
15 ppm, qth = 10 ÷ 25 ppm, Ju = 0.45 ÷ 0.7, Jth
= 0.3 ÷ 0.6, qu/qk = 9 ÷ 15, qth/qu
= 2 ÷ 3, F < 0.6. This type of anomaly may be concerned with the
graphitization alteration.
Synthesizing
the results of pattern recognizing by Bồng Miêu, Trà Giang mines, defined
geophysical anomalies and other geological data, we have contoured 6
perspective on primary gold areas (Fig. 1),
such as:
a. Bồng Miêu perspective area (I): covering almost the
present Bồng Miêu gold mine and extending southward to Xeo Kcheo Village. The anomalies are distributed
mainly at Núi Kẽm and Hố Gần sites, besides, there is a small area of 0.3 km2
at Xeo Kcheo, in 4 km south of Núi Kẽm and Hồ Gần mines, which has anomaly
features like the above mentioned mines.
b. Trà Dương perspective area (II): extending in the
subparallel direction from Trà Dương to Dương Yên, with 13 km in length, 2,8 km
in width, located in the rocks of the Lower Khâm
Đức Subformation, close to the northern edge of II-order Long Bình – Núi Chè
fault. The fault system and zones of mylonites is very complicated.
Almost all the anomalies
in this area belong to the 2nd type. The results of pattern
recognization conform to Bồng Miêu mine with confidence probability of > 80 %.
In this area the mineral
evaluation at scale of 1/10,000 is carried out in an area of 10 km2 in
Trà Dương Commune, besides, there is 1 gold occurence found in Dương Yên.
c. Núi Nưa perspective area (III): extending
in NE-SW direction along the fault of the same direction with 10 km in length
from Hương Lam to Thôn Một, about 2 km in width. This perspective area is
mainly located in the Lower Khâm Đức
Subformation.
In this area are
distributed anomalies of the 2nd type. The results of pattern
recognization conform to Bồng Miêu mine with confidence probability of > 85
%, concentrated at 3 small sites, namely Hương Lam, Đèo Liễu and Thôn Một ones.
According to [1] 1 gold
occurrence has been found at Thôn Một.
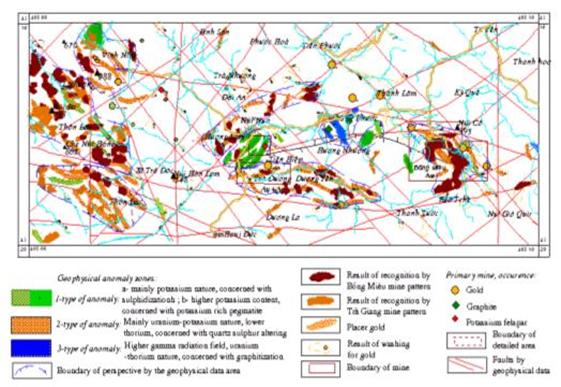
Figure 1. The
result of mineral resource perspective evaluation of Tiên Phước area
d. Thôn Ba (Trà Đốc Commune) perspective area (IV): located
in the south of the investigated area, extending in the subparallel direction
of 8 km in length, 3 km in width,
closer to southern edge of II-order Long Bình - Núi Che Fault. In the north of
the area are distributed the rocks of the Lower Khâm
Đức Subformation, whereas in the south there is the Middle Khâm Đức
Subformation. The fault system is mainly of
NW-SE, NE-SW and subparallel directions.
In this area are
distributed the bands of 2nd
and 1st anomaly types. The results of pattern recognization conform
to Bồng Miêu mine with confidence probability of > 85 %, whereas some places are conform to
Trà Giang mine with confidence probability of
> 80 %.
e. Thôn Bốn (Trà Đốc Commune) perspective area (V):
located close to the western edge of investigated area, extending in NW-SE
direction, with the size of 11×4 km, close to the northern edge of the Long
Bình - Núi Che Fault. In this area, the rocks belong mainly to the Lower Khâm Đức Subformation, in the centre appear
magmatic massifs of the 2nd phase of Quế Sơn Complex. The fault
system is rather complicated.
In this area the
geophysical anomalies are mainly of 1st and 2nd types.
The results of pattern recognization conform to Bồng Miêu and Trà Giang mines
with confidence probability of > 85
%, distributed almost at Thôn Bốn village and Núi Ba Mt.
h. Vĩnh Ninh (Tiên Lãnh Commune) perspective area (VI):
located in the northwest of the area, of isometric form with the size of 5 ×
4,5 km. The rocks belong mainly to the Lower and Middle Khâm Đức Subformations,
located close to the eastern part the intrusive massif of Hải Vân Complex. The
fault system is very complicated.
In this area are
contoured the anomalies of magnetic field ∆T = -270 ¸ 185 nT, the gamma
anomalies of 1st and 2nd types with high potassium
content, probably concerned to potassium pegmatite bodies. The results of
pattern recognization conform to Bồng Miêu mine with confidence probability of
> 85 % and in some places to Trà Giang mine with confidence probability
of > 80 %.
In this area is
discovered 1 gold occurrence close to the side of the Tranh River.
Besides, there are
contoured 1 location of 3rd anomaly type, located in the same Hương
Nhượng graphite mine and the 2 locations of 1st anomaly type with
high potassium content, probably concerned to potassium pegmatite bodies, among
them there is the location coinciding with the Tiên Hiệp potassium feldspar
mine.
3. Results of detailed works
The authors
carried out the detailed investigation in the 2 areas, namely Núi Nưa and Thôn
Ba of Trà Đốc Commune, using geological observation, prospecting the heavy
minerals in limited volume.
a. Results of Núi Nưa perspective area. The detailed work is carried out in an area of about 5 km2
per total 20 km2 of the whole Núi Nưa area.
In this area there are mainly gneiss, biotite gneiss, biotite
schist of the Khâm Đức Formation. The fault system is rather complicated,
including tectonic mylonitization zones. The main direction of the faults is
NW-SE and submeridional.
In this area
were discovered 3 zones of thermal alterion, extended in the NW-SE direction with
the length of 300-750 m, the width of 30-100 m. The hydrothermal altering
processes are usually the quartzitization, sericitization, beresitization. In
the hydrothermal zones are located the sulphide quartz veins with the 10-50 cm
thickness gold veinlets in submeridional or NW-SE direction. The average
content of sulphide is about of 10 ÷ 12 %. The analytical results 7/20 samples
have gold content of 12.5 ÷ 13.3 g/t, silver content of 20 ÷ 21 g/t.
Results of detailed works in Thôn Ba village (Trà
Đốc Commune) perspective area. The detailed work is carried out in the area
of about 6 km2 per 24 km2 of the whole Trà Đốc area. The results show that there are 3
hydrothermal zones, extended in 300-1000 m, the width varies from several to
50-70 m. In the altered zones there are systems of ore dykes of 1-2 m in
thickness. The mineralization is mainly of gold sulphide quartzitization, the
content of sulphide is high of 20-40 %. The main altering processes are
quartzitization, sericitization, beresitization ....
The main rocks are gneiss, biotite gneiss, biotite schist of Khâm Đức
Formation. Besides, there are small massifs of biotite granite of the Hải Vân
Complex, scatteredly distributed in the area. The fault system is rather
complicated, including the mylonitization, cataclastic zones. The analytical
results of 50 samples: 35 samples have gold content of 4 ÷ 102 g/t, silver content 9 ÷ 31 g/t.
IV. CONCLUSIONS
The mathematical methods
of statistical processing the airborne gamma-ray spectrometer and gravimeter data
for the geological and mineral investigation were applied in the Division of
Geophysics in many years, a part of them has been used in prospecting a lot of
important mineral mines. The results of data processing and the detailed work
obtained in the Tiên Phước area, although with restricted volume and methods,
show the objectiveness and the effectiveness of the presented method system.
The authors of this
article hope that the obtained results may be applied in the other fundamental
investigation fields, such as: evaluation of underground water resource,
environmental fundamental investigation for the purpose of planning and
sustainable socio-economic development.
This article
is completed with the support of the basic research projects Nos. 7.200.06 and
7.201.06
REFERENCES
1. Cát Nguyên Hùng (Ed.),
1999. Geological and mineral resource map, scale of
1:50.000, Quảng Ngãi sheet group. Geol. Archives, Hà Nội (in Vietnamese).
2. Grant F.S., G.F. West, 1994. Interpretation theory in applied
geophysics. McGraw - Hill Book Comp., New
York.
3. Lê Đức Hùng (Ed.), 1985.
Results of perspective evaluation of primary gold in Bồng Miêu, Quảng Nam -
Đà Nẵng, scale of 1:10.000. Geol. Archives,
Hà Nội (in Vietnamese).
4. Mai Thất (Ed.),
1991. The
prospecting and evaluation of primary gold in Trà Dương area, Trà My district,
Quảng Nam
province. Geol. Archives. Hà Nội (in
Vietnamese).
5. Nguyễn Tài Thinh, Nguyễn Thế Hùng, Nguyễn Trường
Lưu, Đỗ Tử Chung, 2005. The method system
of processing of the airborne gamma-ray spectrometer and gravimeter data for
evaluating and prospecting the mineral resource. Proc. of Việt Nam
Tech.-Sci. Conf., p. 551-561. Hà Nội.
6. Nguyễn Tài Thinh et
al., 2005. Report
on Basic research project "Study and definition of characteristics of the
geophysical fields (magnetic, radiometric, gravimetric fields) concerning with
the internal alteration and the minerals. Pilot application on the field (Kon
Tum area). Ministry of
Sci. and Techn., Hà Nội (in Vietnamese).
7. Nguyễn Thành Tín, 2006. Geological and mineral features
of Trà Giang gold occurence, Trà My district, Quảng Nam province. Geol. Archives, Hà Nội (in Vietnamese).
8. Nguyễn Văn Trang (Ed.), 1996. Geological and mineral resource map of Hội An
sheet, scale of 1:200.000. Geol. Dept. of Việt Nam,
Hà Nội.
9. Nikitin A.A., 2002.
Spectral-correlation analysis of geophysical data. Moscow State
Geol. Prosp. Inst. (in Russian).
10. Petrov A.B., 1996. Multisignal information valuation
of geophysical fields. Geology and Prospecting, 6 (in Russian).
11. Trương Khắc Vy (Ed.), 1991.
Geological and mineral resources map, scale of 1:50.000, Tam Kỳ - Hiệp Đức
sheet group. Geol. Archives, Hà Nội (in
Vietnamese).
![]() , j =
, j = ![]() , with size of M*N points, where M: number of points on
profile, N: number of profiles.
, with size of M*N points, where M: number of points on
profile, N: number of profiles.